|
A recent study conducted in mice models showed that a two-week course of treatment with cannabinoids (CBD) helped clear amyloid plaques, which are the pathological hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), helping to improve cognition in an experimental model of early onset familial AD.1 The investigators reported that for the first time CBD normalized levels and function, improving cognition as it also reduced levels of the immune protein IL-6, which is associated with the high inflammation levels found in Alzheimer’s. Although the conventional AD treatments such as acetylcholine esterase inhibitors can alleviate the symptoms, these drugs cannot delay the progression or reverse the disease. It has been shown that plant-derived terpenoids, like cannabinoids, possess therapeutic potential to effectively treat AD; terpenoids are part of a large class of naturally occurring organic chemicals.2
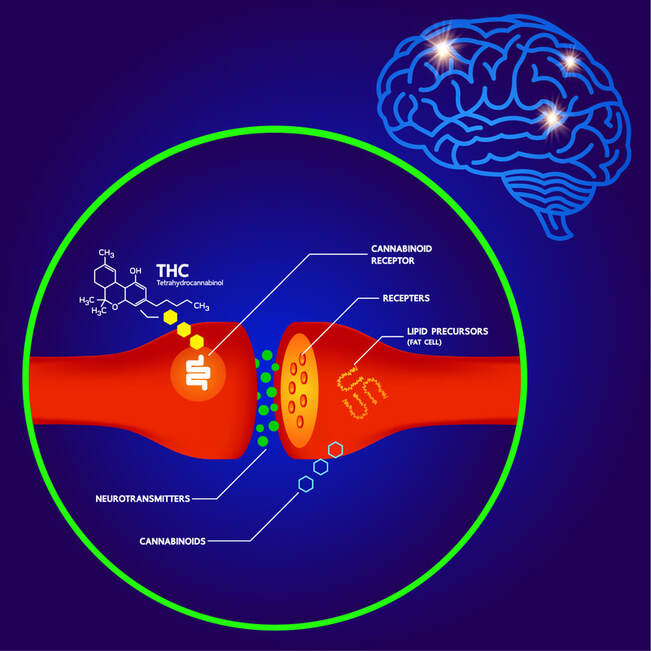
Localized inflammation and generation of excessive Aβ fragments can cause neurotoxicity. ECS in normal and AD brains The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a molecular system responsible for regulating and balancing many processes in the body, including immune response, communication between cells, appetite and metabolism, memory, and more. The endocannabinoid system is powerful and nearly ubiquitous in the nervous system. The cannabinoid receptors dispersed throughout many brain regions are responsible for regulation of numerous aspects of neuronal activity.3
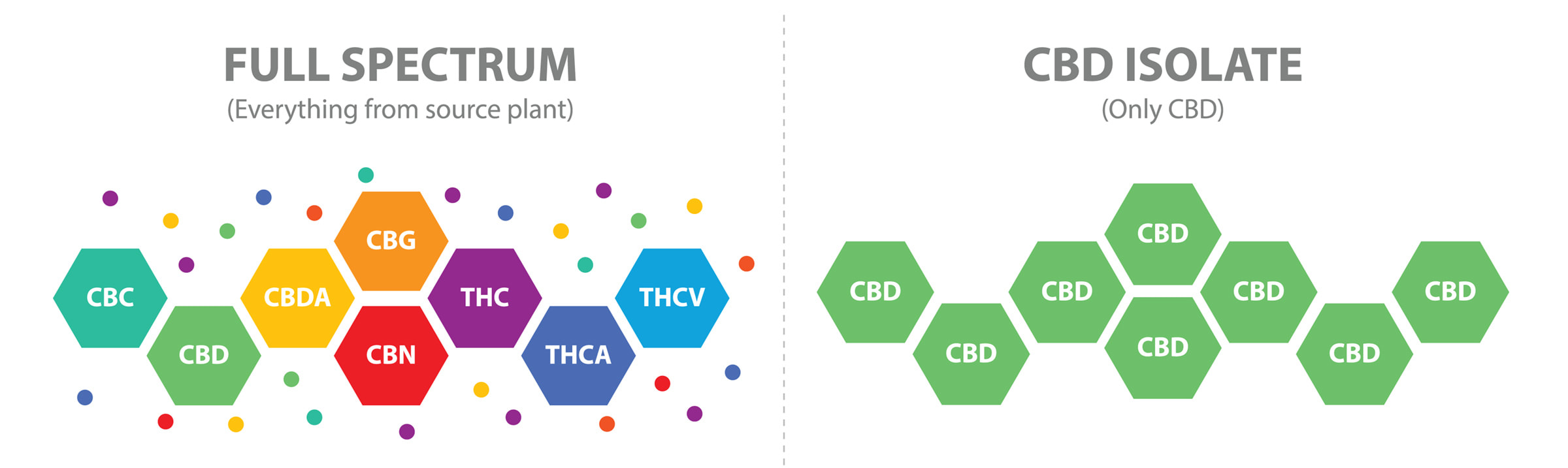
I have discussed before the mechanism of glutamate and excitotoxicity that underlies neurodegeneration that drives many neurological symptoms. Cannabinoids can directly regulate and normalize activation of NMDA receptors, which are proteins found in the membrane of nerve cells that receive signals across the synapse from a previous nerve cell. Cannabinoids can directly increase brain-derived neurotrophic factors; upregulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor can promote neurogenesis and memory performance. CBD also reduces inflammation in the central nervous system as well as oxidative stress. Because of these two mechanisms, CBD is neuroprotective and in some studies with a combination tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) formulation has been proved to be a potent inhibitor of Aβ aggregation.5 But Not All CBD is Created Equal These days, it seems like you can obtain CBD just about anywhere. As of 2018, with the passage of the Farm Bill, federal law legalized hemp-derived CBD containing less than 0.3% THC (note: some state-specific regulations may prohibit its use or sale so it’s advisable to know your state’s laws). Approved hemp-derived CBD contains no psychoactive qualities and is generally considered to be safe. However, just as with any nutraceuticals and supplements, always look for a product that reflects high quality manufacturing standards:
If you are considering adding CBD to your regimen with the guidance of your physician, choose a product intended for oral consumption (e.g. sublingual drops) vs. a topical lotion or salve. I have found that the keys to success with CBD use also lie in choosing the right dose. And if the body is very inflamed from poor nutrition, high levels of stress, bad lifestyle habits (e.g. smoking or excessive alcohol use), know that the efficacy of any CBD will be reduced. Brain Benefits of CBD
What we recommend. A target dose of 40-60mg/day with a maximum dose of 200mg/day of a full-spectrum product (we recommend and carry CYTOGEN™ - 6000, available only through healthcare practitioners). Full-spectrum CBD products contain small amounts of other cannabinoids such as THC (in only the maximum allowable amount per federal law) as well as flavonoids and terpenes, which are beneficial compounds that provide unique scents and flavors. The combination and synergy is truly the magic in these proprietary selections. Day 1 – Day 7 Administration: administer sublingually (under the tongue) and swish around cheeks for max absorption for 90 seconds to two minutes then swallow solution after time lapse. Morning: CYTOGEN 6000mg Tincture – take .25mL with or after breakfast. (12.71mg CBD) Afternoon: CYTOGEN 6000mg Tincture – take .5mL with or after lunch. (25.42mg CBD) Evening: CYTOGEN 6000mg Tincture – take .5mL with or after dinner (25.42mg CBD) Total full-spectrum CBD – 63.55mg CBD Day 8 – Day 21 Administration: administer sublingually (under the tongue) and swish around cheeks for max absorption for 90 seconds to two minutes. Simply swallow the solution after time lapse. Morning: CYTOGEN 6000mg Tincture – take .5mL with or after breakfast. (25.42mg CBD) Afternoon: CYTOGEN 6000mg Tincture – take .75mL with or after lunch. (38.13mg CBD) Evening: CYTOGEN 6000mg Tincture – take 1.0mL with or after dinner (50.84mg CBD) Total full-spectrum CBD – 114.39mg CBD Day 22 Reevaluate to mark progress and adjustments As always, we strongly encourage you to talk to your healthcare practitioner to ensure that even the highest quality CBD product is appropriate to any health conditions and current prescribed medications. And remember too that while there are identified neuroprotective benefits, taking more than the suggested dose is never advisable. But there does seem to be a place for CBD in our toolkit of resources that may help us in the fight against Alzheimer’s and other neurological disease. Questions or comments? Please don’t hesitate to reach out and let us know how we can help!
In hope and healing, Dr. Suzanne Gazda References: 1 Khodadadi H, Salles ÉL, Jarrahi A, et al. Cannabidiol Ameliorates Cognitive Function via Regulation of IL-33 and TREM2 Upregulation in a Murine Model of Alzheimer's Disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2021;80(3):973-977. doi:10.3233/JAD-210026 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33612548/ 2 Yoo KY, Park SY. Terpenoids as potential anti-Alzheimer's disease therapeutics. Molecules. 2012;17(3):3524-3538. Published 2012 Mar 19. doi:10.3390/molecules17033524 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6268347/ 3 Maroon J, Bost J. Review of the neurological benefits of phytocannabinoids. Surg Neurol Int. 2018;9:91. Published 2018 Apr 26. doi:10.4103/sni.sni_45_18 4 Skaper SD, Di Marzo V. Endocannabinoids in nervous system health and disease: the big picture in a nutshell. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012;367(1607):3193-3200. doi:10.1098/rstb.2012.0313 5 Watt G, Karl T. In vivo Evidence for Therapeutic Properties of Cannabidiol (CBD) for Alzheimer's Disease. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:20. Published 2017 Feb 3. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00020 6 Food and Drug Administration https://www.fda.gov/news-events/fda-voices/better-data-better-understanding-use-and-safety-profile-cannabidiol-cbd-products Additional reading: Healthline: The ECS. https://www.healthline.com/health/endocannabinoid-system
0 Comments
Your comment will be posted after it is approved.
Leave a Reply. |
AuthorDr. Suzanne Gazda, Integrative Neurology Archives
February 2024
Categories |


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed