Clinical history: He received his first COVID vaccine in May 2021 and after this he was not well and had to see a cardiologist for lingering cardiovascular symptoms. After the second injection in June 2021, the family noticed confusion and personality change and his Parkinson’s’ disease severely worsened such that he was now needing to use a wheelchair. Although he never fully recovered from these side effects after the first two vaccinations, he received another vaccination in December 2021. Two weeks after the third vaccination (second vaccination with BNT162b2), he collapsed and died a few weeks later. Autopsy report findings: Heart: chronic cardiomyopathy and mild acute lympho-histiocytic myocarditis and vasculitis of small vessels of the heart. Brain: A. acute lymphocytic vasculitis (Lymphocytic vasculitis is characterized by an inflammatory cell infiltration and necrosis of small and medium sized blood vessels that can be found in the brain, spinal cord, and the meninges). B. multifocal necrotizing encephalitis of unknown etiology. C. pronounced neuroinflammation including glial and lymphocytic reaction. Immunohistochemistry for SARS-CoV-2 antigens (spike protein and nucleocapsid) revealed that the lesions with necrotizing encephalitis as well as the acute inflammatory changes in the small blood vessels (brain and heart) were associated with abundant deposits of the spike protein SARS-CoV-2 subunit but no nucleocapsid was observed. Note: Spike protein was also found in the thoracic and abdominal aorta and iliac branches, as well as the cerebral basal artery. The photos in the study that I encourage you to view are stunning, and this is one where spike protein is found in the endothelial lining of vessels and glial cells (glial cells in the central nervous system include oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, ependymal cells, and microglial cells). But it’s significant that no nucleocapsid protein was found. Discussion: As noted above, this case study shows the subacute clinical deterioration of a patient and his eventual death after a series of three COVID vaccinations given over a mere seven months. Not only did he develop severe cardiovascular symptoms after his first vaccination, but he also then had profound advancement of his neurodegenerative disease over a mere 3 months. At no time did he have any underlying infection and since no nucleocapsid protein could be detected, the presence of spike protein must be ascribed to vaccination rather than infection. The spike protein, notably the S1 segment, is likely the major pathogenetic factor leading to post-vaccine syndrome (5, 6). We know that the S1 protein is profoundly toxic. A study by Frank et al published in Brain Behavior and Immunity February 2022 (21) showed that spike protein could act as an independent pathogen to induce microglial cell activation and neuroinflammation. There are vast and numerous intersecting and overlapping pathophysiologic processes contributing to the neurological spectrum of vaccine injuries that I have reviewed at length in my blogs at: https://www.suzannegazdamd.com/blog---long-covid Here, in this case report, spike protein was found throughout the body and brain and especially in the small arteries including the cerebral basal artery which provides blood supply to a critical part of the brain called the brainstem. The Trojan Horses Lingering spike protein and other viral fragments can have very harmful effects to the brain and CNS. We know that spike protein can on its own cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB) (19, 20). In fact, Dr. Bruce Patterson found spike protein in nonclassical monocytes for up to 15 months post vaccination (17, 18) and a study by Bansal found spike protein in exosomes up to four months (15). Under normal circumstances, the BBB filters out the circulatingmonocytes from the brain tissue, but when the brain is inflamed, these immune cells take up residence in the brain (10). Exosomes have bidirectional movement and deliver their cargo, in this case of spike protein, into the brain milieu. Spike protein also has been found in plasma a year post infection, on thrombi, heart muscle, skin cells (22, 23, 24, 25). mRNA has been found in CSF, lymph nodes and in muscle tissue (25, 26, 27, 28). During these time frames of existence, mRNA likely retains its ability to induce spike protein. The lipid nanoparticles designed to protect the mRNA cargo of the COVID vaccinations also easily cross the BBB (4). Biodistribution studies in rats with the mRNA-COVID-19 vaccine BNT162b2 also showed that the vaccine does not stay at the injection site but is distributed to all tissues and organs, including the brain (12) One way or another, we must assume that the toxic spike protein and mRNA are getting into the brain and, most importantly, it’s lingering and creating, as in this case, a subacute deterioration due to cascading mechanisms of injury. For more information, see my blog https://www.suzannegazdamd.com/blog---long-covid/long-covid-but-no-lingering-virus The Five Horsemen of Injury: a looming apocalypse. I have written about key mechanisms of injury in my blog The Five Horsemen: https://www.suzannegazdamd.com/blog---long-covid/the-five-horsemen These mechanisms include:
In this case we saw:
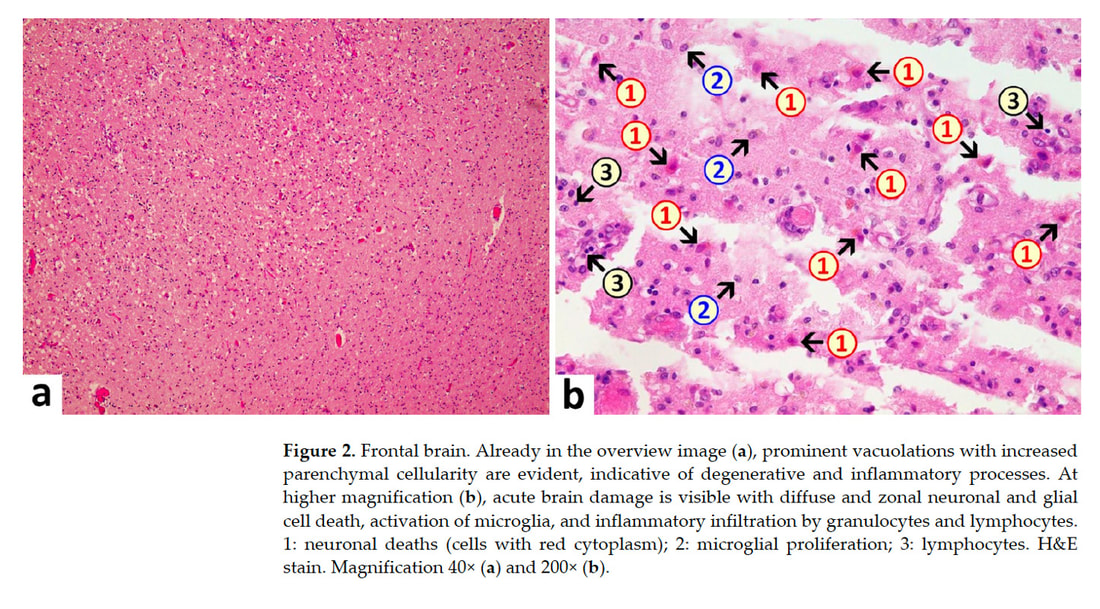
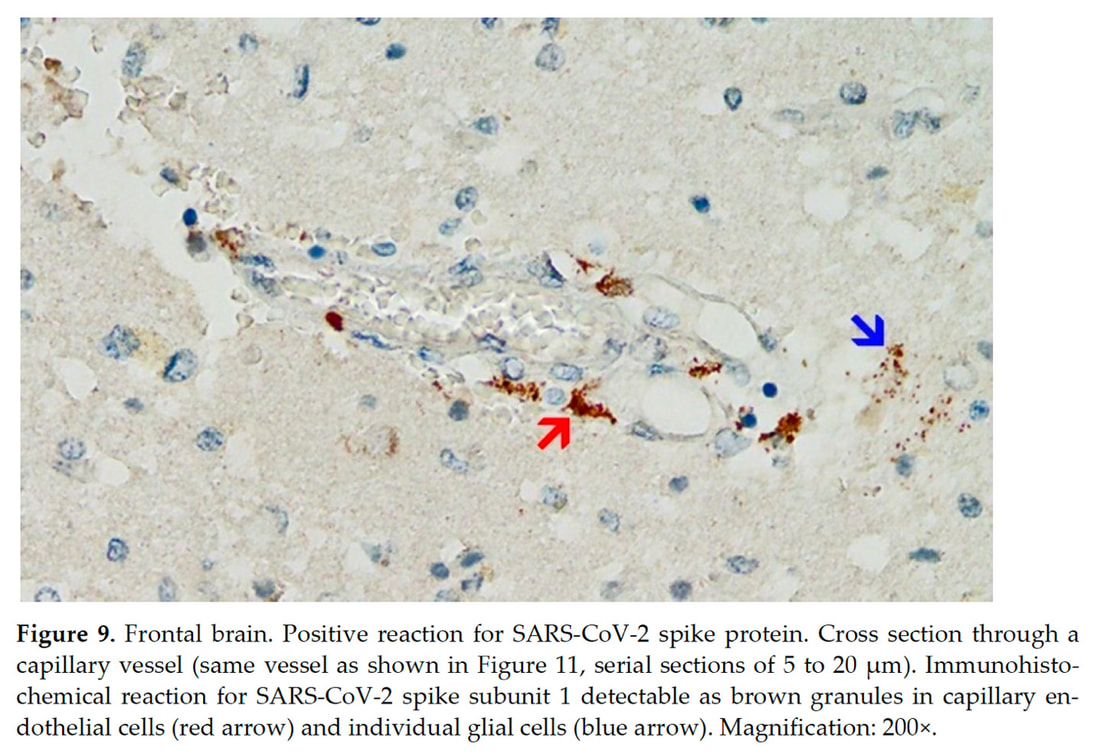
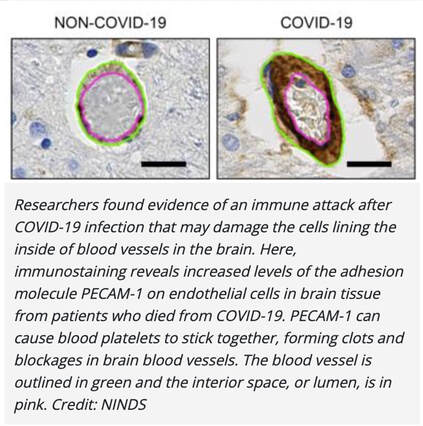
Taken from “A Case Report: Multifocal Necrotizing Encephalitis and Myocarditis after BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccination against COVID-19” showing chronic neuroinflammation, microglial cell activation and cell death. Spike protein will bind to neurons and glial cells which express ACE2 receptors in the CNS, and recent studies suggest that activated glial cells contribute to neuroinflammation (1). Glial cells are the most abundant cells in the central nervous system. There are four types of glial cells including oligodendrocytes which form the myelin sheath around axons, astrocytes that provide nutrients to neurons, maintain their extracellular environment, and provide structural support, microglia which scavenge pathogens and dead cells and ependymal cells which produce cerebrospinal fluid that cushions the neurons. A recent study published by Planton et al in the BMJ, suggests that neuronal and glial degeneration can occur in patients with COVID-19 regardless of overt clinical neurological manifestations (9). It is now possible to measure CNS damage with blood tests called serum neurofilament light chain (sNfL) and glial fibrillar acidic protein (sGFAp), which are reliable biomarkers of neuronal and glial injury. As we have continuously emphasized, chronic neuroinflammation is the downfall of the brain and contributor to virtually every related disorder. b. Acute Lymphocytic vasculitis Vasculitis is inflammation of blood vessels. In individuals with vasculitis, inflammation damages the lining of affected blood vessels, causing narrowing, the formation of blood clots (thrombosis), and/or blockage. Lymphocytic vasculitis is characterized by an inflammatory cell infiltration and necrosis of small and medium sized blood vessels. The specific underlying cause of vasculitis is not fully understood. However, in most cases, vasculitis is thought to be due to disturbances of the body’s immune system (i.e., an autoimmune attack on the blood vessels). Vasculitis in the brain can cause widespread neuroinflammation and as well increase the risk of thrombotic or hemorrhagic stroke. CNS vasculitis can present with a wide variety of neurological symptoms from brain fog, confusion, seizures, neuropathy, vision changes paralysis, headache and more (11). Taken from “A Case Report: Multifocal Necrotizing Encephalitis and Myocarditis after BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccination against COVID-19” showing spike protein laden in endothelial cells lining a blood vessel and attached to neurons called glial cells. SARS-CoV-2 spike protein impairs endothelial function via downregulation of the ACE2 receptor (6,7). Endothelial cells line all blood vessels and provide a key stronghold to the BBB. Endothelial dysfunction is known to be highly involved in organ dysfunction induces a pro-coagulant state, microvascular leak, and organ ischemia. No thrombi or clotting were observed in this case, although diffuse atherosclerotic disease was noted. One of the pathophysiological mechanisms in long COVID and post-vaccine injury is likely to be highly levels of vascular inflammation and micro clotting. Spike protein can induce the formation of the amyloid/ fibrin micro clots which are very resistant to fibrinolysis (32). Immune complex vasculitis has been reported in a patients post-COVID 19 vaccinations c. Multifocal necrotizing encephalitis (MNE) MNE is usually provoked by virus-associated febrile illness and rapid clinical deterioration It is thought to be a very rare presentation and is the result of a “cytokine storm” which is a release of high inflammatory cytokines. In the CNS, MNE leads to brain injury through alteration of vessel wall permeability without vessel wall disruption and destruction of the BBB (13). With the development of acute necrotizing encephalitis, brain dysfunctions may present as seizures, disturbance of consciousness, and focal neurological deficits. There may be a prodromal stage and very rarely patients recover but most cases are fulminate and deadly Acute necrotizing encephalitis has also been reported to the diphtheria, tetanus toxoid, and whole-cell pertussis (DPTw) vaccination (13). Intravenous glucocorticoids, immunoglobulin, and plasmapheresis should be effective based on the pathogenesis of AN. Numerous cases have been reported of autoimmune encephalitis and encephalomyelitis after COVID-19 vaccination (29). More Evidence of Immune Downfall from Spike Protein A study published just this summer, “Neurovascular injury with complement activation and inflammation in COVID-19”in Brain, showed autoimmune induced damage to the BBB (31). Antibody-mediated cytotoxicity directed against the endothelial cells is the most likely initiating event that leads to vascular leakage, platelet aggregation, neuroinflammation and neuronal injury. No virus was found, and the researchers proposed that antibodies against the spike protein might bind to the ACE-2 receptor on endothelial cells triggering the cascade of events. It is likely that an indolent immune response is continuing causing neuronal injury. Taken from “Neurovascular injury with complement activation and inflammation in COVID-19” (31) A recent Brazilian study published in the journal PNAS, “Morphological, cellular, and molecular basis of brain infection in COVID-19 patients” (3) describes some of the effects that SARS-CoV-2 can have on the central nervous system. The researchers’ results suggest damage to astrocytes. Findings noted necrosis and inflammation, such as edema neuronal lesions and inflammatory cell infiltrates and on immunostaining, they identified antibodies reacting to mRNA and spike protein – but no virus was found. Astrocytes perform a variety of tasks, from axon guidance and synaptic support to the control of the blood brain barrier and blood flow. Damage to astrocytes will cause neuronal cell death. Were prions involved in this patient’s demise? Please note that in the autopsy report, no mention was made of prion formation; studying this postmortem would have required special staining. Given that this patient had rapid progression of his neurodegenerative disease one wonders if the rapid neurological decline after his second COVID vaccination, could have been triggered by the formation of increasing levels of amyloid fibrils, tau, alpha synuclein, etc? The study by Nystrom et al showed spike protein when placed in cell culture, quickly formed into amyloid fibrils. (33) Photo taken from Amyloidogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein (33)
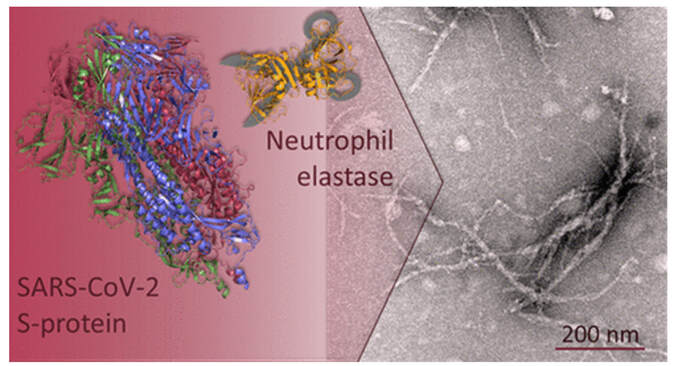
Showing how S-protein is endoproteolyzed by an enzyme called neutrophil elastase which transforms spike protein into amyloidogenic S-peptides Amyloid is a prion and prions self-propagate via cell-to-cell contact and via exosomes. Many neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, Huntington’s, Lewy Body Dementia, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and even multiple sclerosis (MS) are thought to be a result of prion-like activity (34). β-Amyloid peptides can promote the aggregation of α-synuclein and exacerbating α-synuclein-dependent neuronal pathologies like Parkinson’s disease. For more information, see my blog at: https://www.suzannegazdamd.com/blog---long-covid/will-we-see-a-rise-in-neurodegenerative-disease-post-covid-and-post-covid-vaccines A Smoking Gun: the implications learned from this case report. The authors of this study state “the presence of spike protein but no nucleocapsid protein in the heart and brain of the current case can be attributed to vaccination rather than to infection. This agrees with the patient’s history, which includes three vaccine injections, the third one just weeks before his death, but no positive laboratory or clinical diagnosis of the infection.” Spike protein looks eerily like the body and brain and in a study by Vorjdani and colleagues, 28 out of 55 human tissues reacted via molecular mimicry and shared homology against spike protein and other viral fragments setting the stage for a barrage of autoantibodies that can attack the body and brain ((14). Spike protein is highly thrombogenic. It causes alteration of immune health with high levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines driving chronic neuroinflammation that can lead to neuronal injury and death. Spike protein can induce the formation of amyloid and other prions. This patient’s tragic death was likely due to multiple factors induced by lingering, accumulating and rising levels spike protein and subsequent downstream effects, over a mere seven months following administration of the COVID vaccinations. Millions have been injured around the world. Sadly, thousands upon thousands have died. The tsunami is here – and this study is absolute proof. Here is the smoking gun. I extend my sincerest condolences to the family of this patient. In hope and healing, Dr. Suzanne Gazda Study: Mörz M. A Case Report: Multifocal Necrotizing Encephalitis and Myocarditis after BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccination against COVID-19. Vaccines. 2022; 10(10):1651. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10101651 Study references:
Additional references: Frank MG, Nguyen KH, Ball JB, et al. SARS-CoV-2 spike S1 subunit induces neuroinflammatory, microglial and behavioral sickness responses: Evidence of PAMP-like properties. Brain Behav Immun. 2022;100:267-277. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2021.12.007 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8667429/ Lee MH, Perl DP, Steiner J, et al. Neurovascular injury with complement activation and inflammation in COVID-19. Brain. 2022;145(7):2555-2568. doi:10.1093/brain/awac151 Mücke, V.T., Knop, V., Mücke, M.M. et al. First description of immune complex vasculitis after COVID-19 vaccination with BNT162b2: a case report. BMC Infect Dis 21, 958 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12879-021-06655-x https://bmcinfectdis.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12879-021-06655-x Tirotta, D. et al. Cutaneous small vessel vasculitis associated to palpable purpura after Covid 19 Vaccination: a case report and a literature review. Research Square. (2022) https://assets.researchsquare.com/files/rs-1359700/v1/13715b44-2bc2-43f7-ae7e-3de1d1453adc.pdf?c=1658260295 Kim BC, Kim HS, Han KH, Han SY, Jo HA. A Case Report of MPO-ANCA-Associated Vasculitis Following Heterologous mRNA1273 COVID-19 Booster Vaccination. J Korean Med Sci. 2022 Jul;37(26):e204. https://jkms.org/DOIx.php?id=10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e204 Gazda, S. The Five Horsemen. (August 24, 2022). https://www.suzannegazdamd.com/blog---long-covid/the-five-horsemen Masliah, E. et al. β-Amyloid peptides enhance α-synuclein accumulation and neuronal deficits in a transgenic mouse model linking Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. PNAS. (2022) https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.211412398 Gazda, S. Alpha-synuclein in neurodegenerative disease. (October 2020). https://www.suzannegazdamd.com/scientifically-speaking1/alpha-synuclein-in-neurodegenerative-disease See our long COVID series at: https://www.suzannegazdamd.com/blog---long-covid
0 Comments
Your comment will be posted after it is approved.
Leave a Reply. |
AuthorSuzanne Gazda M.D. Neurologist Archives
January 2024
Categories |


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed