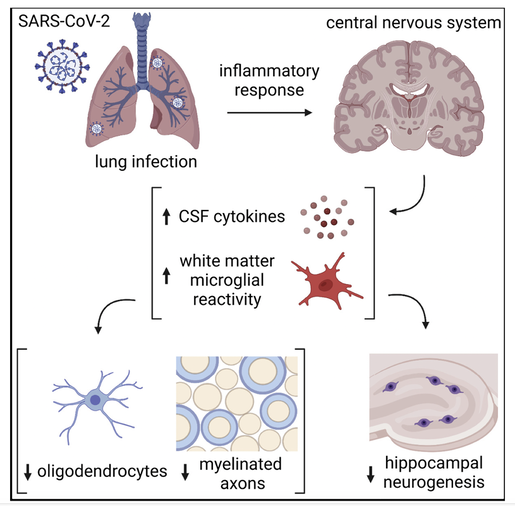
 Dr. Michelle Monje’s team at Stanford has spent two decades studying cognitive impairment after cancer. They uncovered key details in how chemotherapy impairs the function of the brain’s white matter, regions of the brain normally rich in well-insulated nerve fibers that quickly transmit signals from one place to another. Myelin, the fatty coating insulating the long arms of the neurons, helps speed the transmission of nerve signals. In chemo brain, damage to myelin slows their transmission. Now they are looking at brain findings after COVID. Their work was published in June 2022 in "Cell." Mild respiratory SARS-CoV-2 infection can cause multi-lineage cellular dysregulation and myelin loss in the brain https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(22)00713-9 Dr. Monje and her colleagues examined brain changes in mice in which the researchers had induced SARS-CoV-2 infections confined to the respiratory system. Mice lack the cellular receptors that the SARS-CoV-2 virus uses to invade human cells, but animals in the study were genetically engineered to express the necessary receptors in the respiratory tract. After exposure to SARS-CoV-2, the mice had mild infections they did not lose weight or behave as though they were ill, and the virus was not found in their brains. Credit CELL: Volume 185, ISSUE 14, P2452-2468.e16, July 07, 2022 Their findings included:
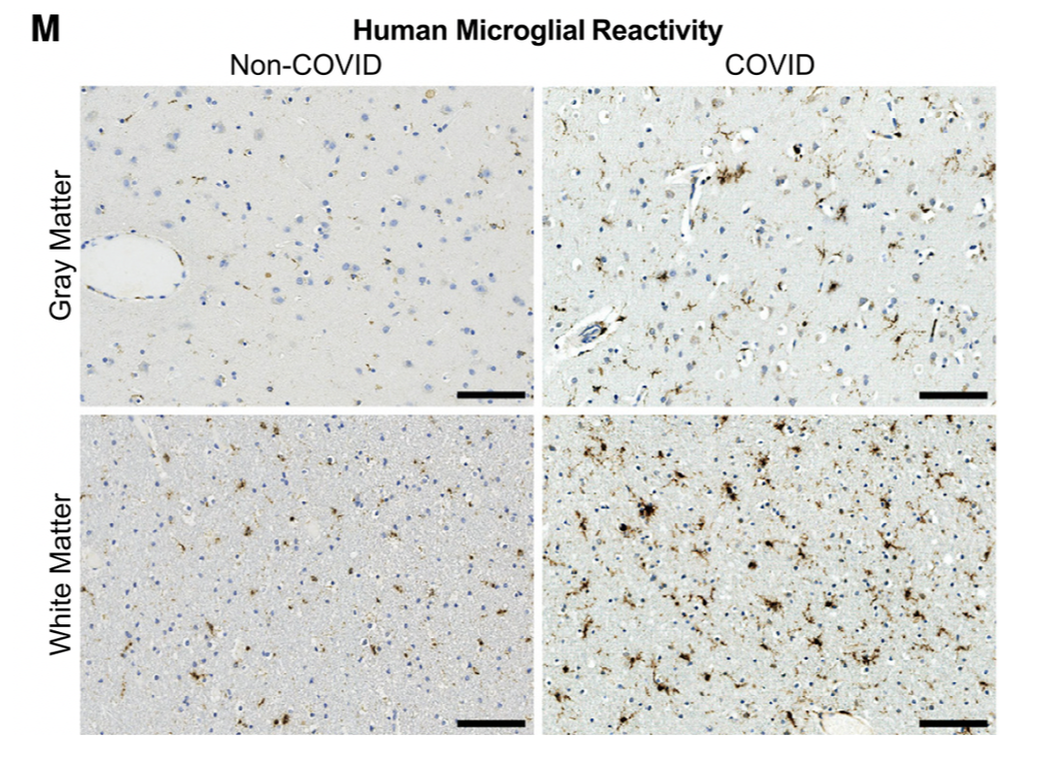
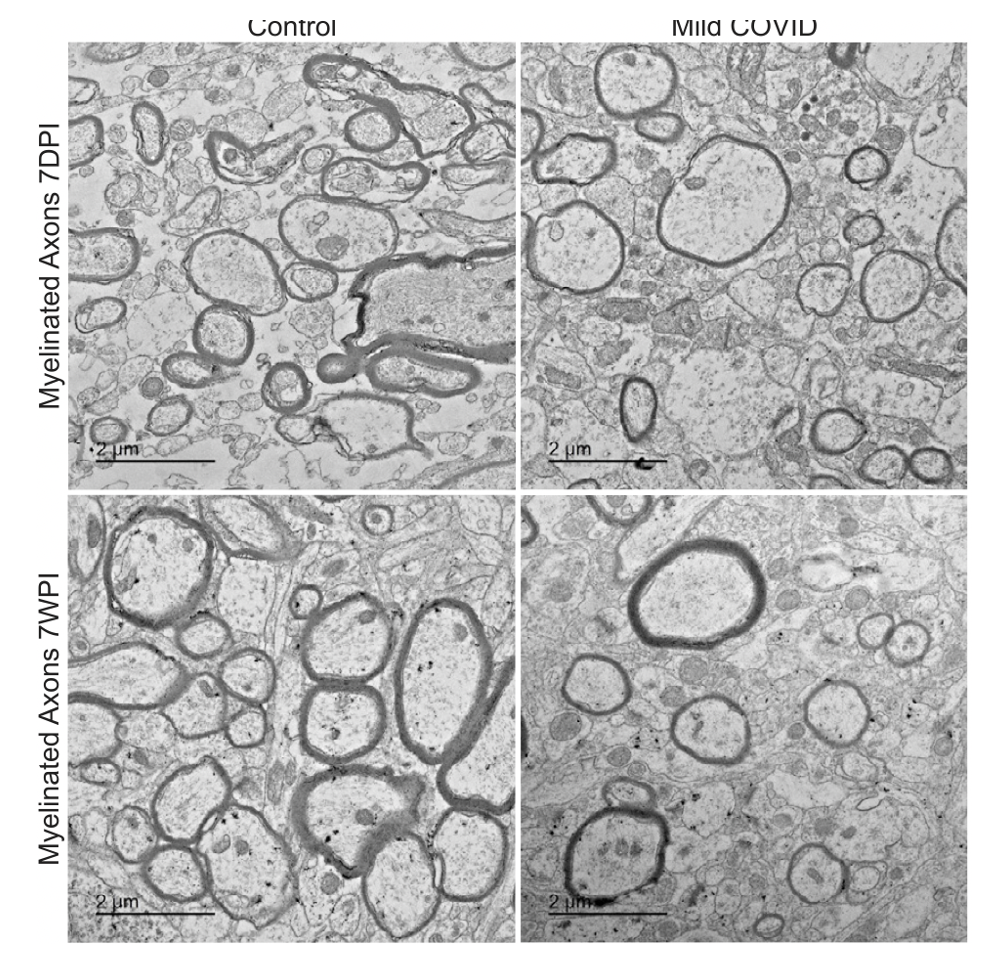
Credit: CELL Volume 185, ISSUE 14, P2452-2468.e16, July 07, 2022 Microglial cell activation was also very high in the subcortical white matter of the brain White matter is found in the deeper tissues of the brain (subcortical). It contains nerve fibers (axons), which are extensions of nerve cells (neurons). Scientists found decreased oligodendrocytes, and myelin loss. Oligodendrocytes are the myelinating cells of the central nervous system (CNS). Myelin gives the white matter its color and it also protects the nerve fibers from injury. When the myelin sheath is damaged, nerve impulses slow or even stop, causing neurological problems. These diagrams are taken from the Monje article. Credit: CELL Volume 185, ISSUE 14, P2452-2468.e16, July 07, 2022 The most common demyelinating disease is multiple sclerosis (MS), an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks myelin of the brain, spinal cord, and/or eyes. Scientists have long regarded the brain's white matter as passive infrastructure, but new work shows that it actively affects learning and mental illness. Credit: CC BY creativecommons.org
Although the researchers at Stanford did not say what was driving these findings, but in this research published Feb 2022 in Brain Behavior Immunity, it was the spike protein that drove neuroinflammation and microglial cell activation. The brain is in big trouble and may help explain why we saw alarming brain atrophy in the UK Biobank study. The U.K. Biobank Study Showed Shrinking Brains post COVID The findings, published in Nature, reveal tissue damage and greater shrinkage in brain areas. The U.K. Biobank is a large-scale biomedical database and research resource that is enabling new scientific discoveries to be made that improve public health and represents data from more than 500,000 study participants.
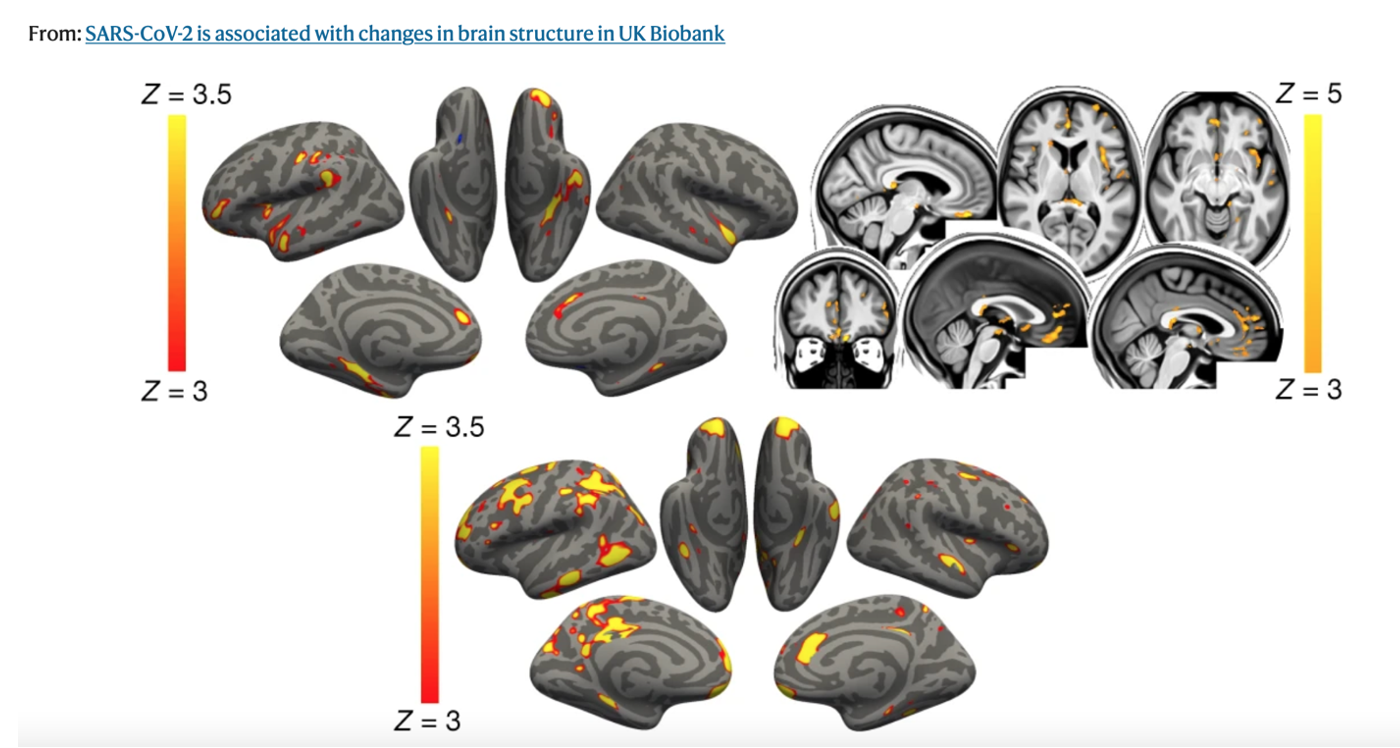
Top, the main analysis shows that the strongest, localized reductions in grey matter thickness in the 401 infected participants compared with the 384 controls are bilaterally in the parahippocampal gyrus, anterior cingulate cortex and temporal pole, as well as in the left orbitofrontal cortex, insula and supramarginal gyrus.
The overlapping olfactory- and memory-related functions of the regions shown to alter significantly over time in SARS-CoV-2—including the parahippocampal gyrus/perirhinal cortex, entorhinal cortex and hippocampus in particular raise the possibility that longer-term consequences of SARS-CoV-2 infection might in time contribute to Alzheimer’s disease or other forms of dementia.
0 Comments
Your comment will be posted after it is approved.
Leave a Reply. |
AuthorSuzanne Gazda M.D. Neurologist Archives
January 2024
Categories |

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed