|
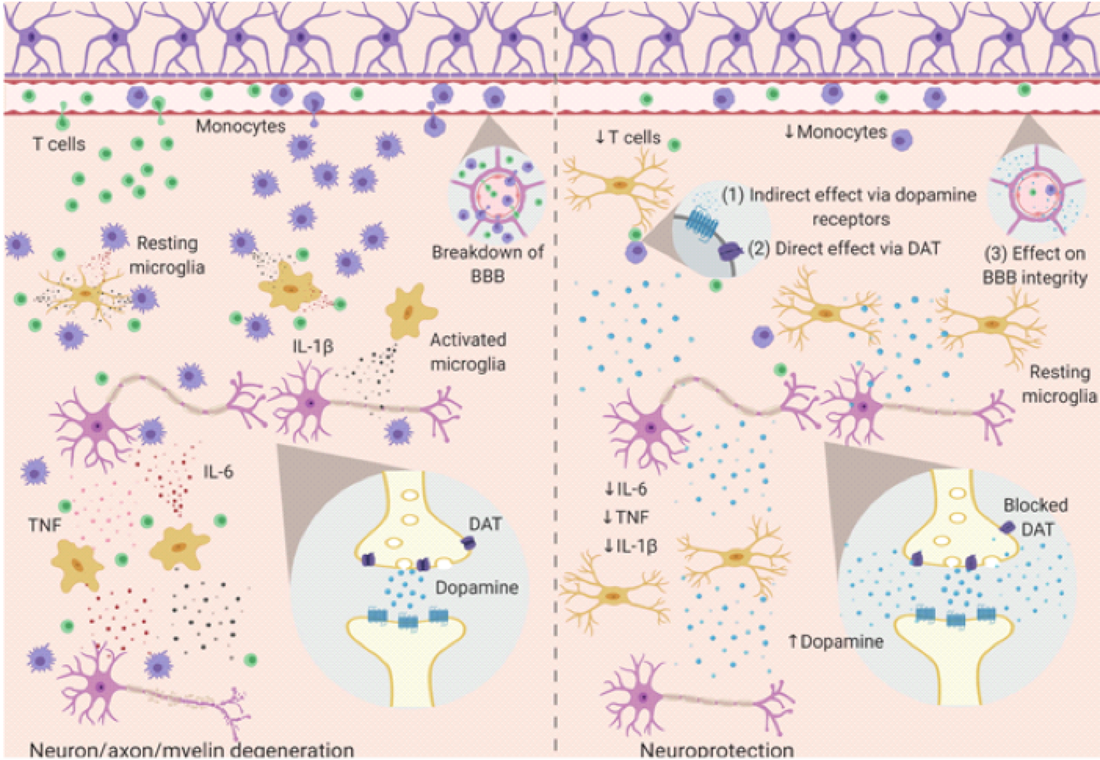
This medication is also commonly prescribed off label for chronic fatigue, ADHD, mood boosting and cognitive enhancement. One of the most common complaints in all patients with autoimmune disease is chronic fatigue. Modafinil is a psychostimulant drug that was approved in 1998 by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of narcolepsy, excessive daytime sleepiness and obstructive sleep apnea. This medication is also commonly prescribed off label for chronic fatigue, ADHD, mood boosting and cognitive enhancement. A recently published article, “Modulating the immune response with the wake-promoting drug modafinil: a potential therapeutic approach for inflammatory disorders” reports on the findings in a 2019 study at the University of Sweden that looked at possible immunomodulatory effects of this medication. The authors stated, “We conclude that there is unequivocal evidence of an anti-inflammatory effect of modafinil in experimental animal models of brain inflammation and neurodegenerative disorders, including systemic inflammation and methamphetamine-induced neuroinflammation, Parkinson’s disease, brain ischemia, and multiple sclerosis." How it works: back to dopamine and other neuro-chemical messengers. I previously have written about the importance of dopamine receptors in PANS and PANDAS conditions. Dopamine is an essential neurotransmitter for many brain actions and helps regulate mood, movement, cognition and behavior - and now we can see that dopamine is clearly tied to the health of the immune system. Dopamine actions: The dopamine D1 and D2 receptors have been considered to be essential in mediating the wakefulness promoted by modafinil. There is a significant affinity of modafinil to the dopamine transporter (DAT). If one blocks the DAT receptor then there will be more dopamine available. The dopamine transporter (DAT) controls the spatial and temporal dynamics of dopamine (DA) neurotransmission by driving reuptake of extracellular transmitter into presynaptic neurons. Norepinephrine actions: Modafinil also affects the central norepinephrine (NE) system by binding to the norepinephrine transporter (NET) and by blocking the reuptake of NE. This serves to help prevent sleep activation in the ventrolateral preoptic nucleus (VLPO), which is a group of sleep-active neurons that has been identified in the hypothalamus of rats and is thought to inhibit the major ascending monoaminergic arousal systems during sleep. GABAergic actions: Modafinil tends to reduce the Gamma-aminobutyric acid-ergic (GABAergic) transmission, which results in increased brain levels of glutamate and serotonin. GABA's role in the brain is reducing neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system and it is well established that activation of the GABA(A) receptors favors sleep. Growing evidence that modafinil does so much more than improve patient fatigue. Additional results that bear continued efforts to investigate modifinil and its diverse application in neurological instances include: Cognitive Enhancement. Studies show that modafinil is beneficial in improving working and recognition memory, attention and other cognitive functions. It has also proven effective in improving cognition in adolescents with ADHD and adults with schizophrenia (Battleday and Brem, 2015 ); Minzenberg and Carter, 2008 ). This might be relevant to the ability of modafinil to increase hippocampal neurogenesis, an effect reported following acute treatment in both laboratory mice and rats. (Brandt et al., 2014 ); Sahu et al., 2013 ). Reduction in Neuroinflammation. Modafinil has been shown to impact specific aspects of the brain immune response, such as monocyte recruitment and activation (Zager et al., 2018 ), T cell differentiation, cytokine production (Brandão et al., 2019 ) and glial activation (Raineri et al., 2012 ). The data from in vivo and in vitro models of neuroinflammation consistently show that modafinil is an effective blocker of microglial activation and consequently of in situ production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and other inflammatory mediators. This makes modafinil a promising therapeutic approach to neurodegenerative disorders in which neuroinflammation plays a significant role. Potential for use in neurodegenerative disease. Relative to use in Parkinson’s disease, Fuxe and colleagues were the first to show that modafinil treatment prevents the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra (SN) and also has neuroprotective effect on GABAergic neurons in the substatia nigra, with a small increase in the number of non-neuronal cells, likely glial cells. Modafinil is commonly prescribed for multiple sclerosis patients and, as shown for the first time by this groundbreaking study, it’s clear that the therapeutic properties are closely linked to an anti-inflammatory effect. The mechanism in mice models revealed: 1. Reduction in the frequency of T helper (Th)-1 cells (which drive autoimmunity against myelin). 2. A drastic decrease in interferon (IFN)-γ. 3. Reduced severity of EAE (experimental autoimmune encephalitis) symptoms. These results provide further indication that modafinil may do much more than just improve fatigue in patients with neurological/ autoimmune problems. Immunomodulation with modafinil. The immunomodulating effects of this drug have been studied extensively and although modafinil has been shown to be pro-inflammatory in peripheral immune cells of naive mice by stimulating IFN-mediated immunity, it has been demonstrated to be anti-inflammatory in animal models of inflammatory diseases. There are now proposed mechanisms that show modafinil may shear up the blood-brain-barrier (BBB) through directly or indirectly influencing the function of the BBB or circumventricular organs, such as the choroid plexus, most likely by affecting its permeability to immune cells and inflammatory mediators. Dopamine and the reward system also has been shown recently to be a new pathway between the brain and immunity. Researchers have shown that increased dopamine, the brain’s pleasure and ‘feel good’ chemical messenger, is linked to improved immune function. This suggests that activities that physiologically stimulate the reward system, such as engaging in sex, social interactions and even physical activity, might have beneficial effects via this newly proposed mechanism when fighting an infection or cancer. Since we know that modafinil increases dopamine levels in the brain, it appears to be a therapeutic option for use beyond addressing fatigue symptoms alone and may offer another immunomodulatory resource for physicians to consider in designing patient protocols. (1) The excessive extracellular dopamine negatively influences the infiltration and activation of immune cells and resident microglia, probably by acting on the dopaminergic receptors of these cells. (2) Direct action of modafinil on DAT expressed by immune cells and glia, which is a mechanism independent of brain dopamine levels Delving into new mechanisms to explain psychoneuroimmunology is leading us down an entirely new level of understanding. After 30 years of study, I continue to remain awestruck at the complexity of the miraculous brain and the opportunities to offer patients more treatment opportunities that can enhance their quality of life. In health, Dr. Suzanne Gazda https://www.researchgate.net/deref/http%3A%2F%2Fdx.doi.org%2F10.1016%2Fj.euroneuro.2015.07.028
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17712350 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25158676/ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4195593/ https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0889159119314953#b0240 https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00452/full https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3464292/ https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0889159119314953#b0240
2 Comments
6/21/2021 09:22:02 am
This drug is supposedly the secret ingredient to all of those "geniuses" or "intellectuals" out there. It's supposed to help you perform better and keep your mind sharper in order to live a productive life. Despite its popularity, there is still a lot of controversy over whether this drug actually works or not. I do admit, that it can help with staying awake during long days and focuses your thought process on the task at hand. The only downside is that it carries with it too many side effects, which may cause some people problems like weight loss and jitters sometimes making them feel uncoordinated when they're taking this drug.
Reply
Your comment will be posted after it is approved.
Leave a Reply. |
Authorby Suzanne Gazda M.D. Archives
August 2021
Categories |
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed